The CIA Triad, which includes Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability, is the core guide in information security. This model has significance in determining how organizations should protect their sensitive data from unauthorized access while ensuring that information remains intact and is accessible to authorized users. The importance of the CIA Triad is that it forms a systematic approach to risk management that allows companies to identify vulnerabilities and establish sound security precautions. Its tenets are applicable across the spectrum of cybersecurity frameworks, making it one of the most indispensable allies for organizations of any size and sector as they navigate the complexities of securing their digital environments.
What is the CIA Triad?
The CIA Triad is basically a starting point or foundation for the cybersecurity principles of information protection. This principle states that data classified under confidential information can only be accessed by authorized users, integrity ensures that the data is correct and in an original state. The availability seems to be the state of information and systems available anytime the user wants to have access. This model aims to provide a standard framework against which the security posture can be assessed and vulnerabilities identified. In general, organizations can reduce security risks, upgrade overall security posture, and comply with regulations under the application of the CIA Triad. CIA is a base cross-functional guideline for many of the cybersecurity-based frameworks that will create uniform and well-rounded strategies for security as per specific organizational needs.
Confidentiality
Part of the CIA Triad involves Confidentiality; that is, allowing sensitive information to be accessed by authorized people. This is very important in preventing access to personal and proprietary data, with a view to unauthorized access and misuse. Key concepts that underpin confidentiality include encryption: securing data at rest and while in transit using algorithms such as AES and RSA, and access control mechanisms that include RBAC and MFA which restrict access based on user roles and require the use of multiple forms of verification. Effective data classification and handling practices will assist organizations in determining the level of sensitivity of information so that appropriate security measures may be applied. For instance, in banking systems, it is a must to ensure that sensitive customer information is protected for the sake of trust and regulations. Similarly, VPNs are used to secure remote access to organizational resources by ensuring confidential information is not intercepted by unauthorized parties. All these strategies can greatly improve data protection efforts while reducing the risks associated with data breaches.
Integrity
The Integrity of data is essential for maintaining the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of information during its entire lifecycle. This principle includes a range of techniques and technologies aimed at safeguarding data against corruption, unauthorized access, and additional risks. Hashing algorithms, especially MD5 and SHA-256, are very critical in data identification in detecting changes because they create hash values that can be judged over time; any hash value change means data must have been modified. Digital signatures are also used for the authenticity of data that proves to everyone that the data originated from a credible source and in its passage, has not changed.
Moreover, using version control and maintaining audit logs are critical practices to track changes and ensure data integrity over time. These systems help organizations ensure that financial transactions remain unchanged and protect sensitive information from corruption in storage and transit. In a world where data breaches are becoming increasingly common, ensuring data integrity is no longer a matter of technical necessity but a critical component of organizational trust and regulatory compliance.
Availability
Availability is one of the core principles in information security; it ensures that information and systems should be available at all times, whenever needed. This demands the use of various techniques and technologies to minimize downtime and ensure uninterrupted access to resources. In this context, some key principles of redundancy and fault tolerance have been implemented; methodologies, for instance, include RAID, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, and regular data backup are applied to avoid possible malfunction of hardware and loss of data. In addition, organizations utilize DDoS mitigation techniques and load balancing to efficiently handle traffic and to ensure services are not rendered unusable due to overflooding requests or threats.
In addition, a disaster recovery and business continuity plan is essential to ensure availability in case of unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or system failures. These plans outline the procedures that need to be followed to quickly restore operations, thus ensuring continuity of services. For instance, 24/7 access to e-commerce platforms is necessary for customer satisfaction and revenue generation, whereas minimizing downtime during cyberattacks or other crises will be important to maintain trust and operational resilience. Finally, by prioritizing availability, organizations can ensure that their services are reliable and effective in supporting their users.
Interconnection of the Triad
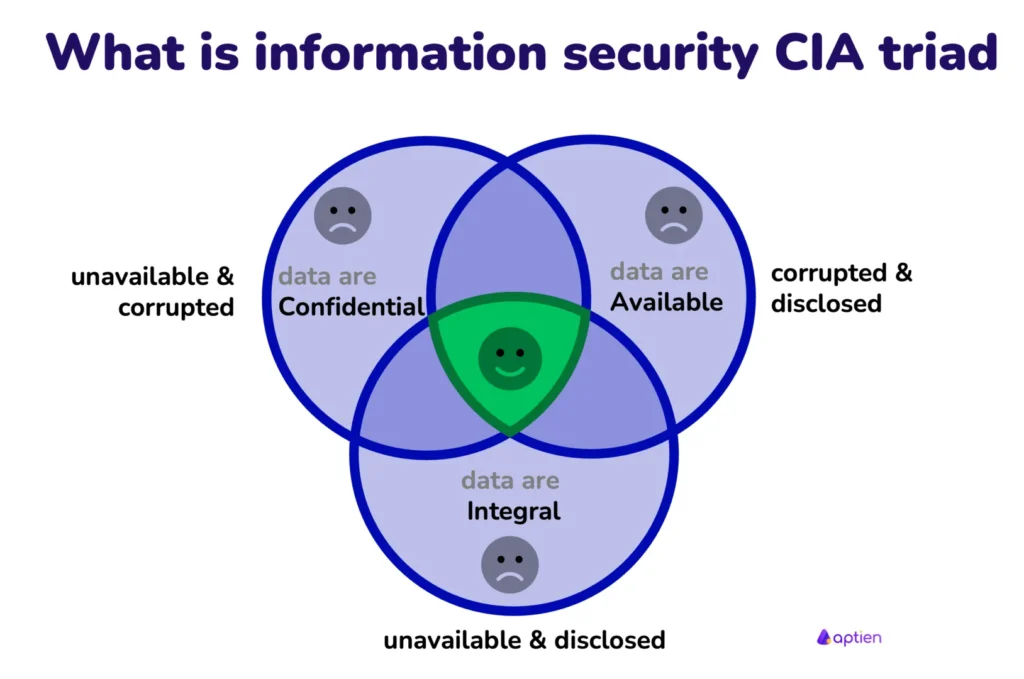
The CIA Triad is one of the seminal information security models that illustrates interdependence. Each component forms a crucial part of ensuring information protection, and each change can have a large impact on the others. For instance, increasing the level of confidentiality through encryption may limit access to data so that its availability to legitimate users may be reduced. Increased availability—such as guaranteeing systems are always on—may compromise confidentiality as access controls are relaxed.
There usually arises a conflict among such aspects when organizations try to achieve them based on their special needs and priorities. A healthcare provider would place the aspect of confidentiality as very important to protect patient’s data, which could conflict with the aspect of time access in case of emergency cases. Similarly, an e-commerce platform may prioritize the aspect of availability to increase sales, and this could expose the confidential data of customers if adequate measures on security are not implemented. Only a holistic approach, therefore, which considers the organization’s goals, regulatory requirements, and changing threats can result in the final balance of the CIA Triad. This is also vital for trust and resilience in an increasingly digital world.
Real-World Applications of the CIA Triad
The CIA Triad refers to Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability, which are necessary in most industries to keep sensitive information safe. Health care is one of the areas in which HIPAA mandates confidentiality as a strict requirement for the protection of patient data, encrypting and access controls to prevent unauthorized access but maintaining integrity through accurate records. For example, electronic health records must be both secure and accessible to authorized personnel for privacy but operational efficiency.
In the finance industry, complying with PCI DSS standards gives great attention to protecting cardholder data. Financial institutions implement high-security protection protocols that provide confidentiality via encryption and tokenization. Integrity is maintained by having periodic audit transactions to detect discrepancies.
In government and defense, the CIA Triad is an important component of national security. Agencies employ stringent measures to ensure classified information is protected; therefore, only authorized people are able to access sensitive data (confidentiality), that data is correct and unchanged (integrity), and critical systems are available during a cyberattack or natural disaster (availability). These real-world applications demonstrate how the CIA Triad forms the foundation for effective security strategies designed for particular regulatory and operational requirements.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the CIA Triad—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—represents the core of cybersecurity, focusing on the critical aspects that have to be covered to protect sensitive information and ensure systems are secure. Its importance goes beyond the protection of data but also to direct organizations in their security strategies and risk management practices. It is from the understanding of the interdependencies within the triad that organizations will have a holistic security framework capable of appropriately addressing potential threats without diminishing operational efficiency.
Since cyber threats are in a constant state of evolution, businesses and individuals need to periodically assess their systems for CIA compliance. This would be proactive in identifying vulnerabilities, strengthening security measures, and eventually helping build a culture of resilience against cyberattacks. We encourage readers to take time to assess their systems to ensure that they comply with the principles of the CIA Triad and, therefore, protect their valuable information assets effectively.



Pingback: AWS Firewall: Protecting Your Cloud Infrastructure - Cynfober