Imagine sending a postcard to someone but anyone can read the private messages that you have written in the postcard. This is how data travels on the internet without encryption. In 2023 alone, 22 billion records were exposed due to data breaches highlighting the urgent need for better security measures.
Data Encryption acts as a digital locker that can be accessed by authorized individuals using a security or a decryption key. Whether it’s securing your online payments, personal chats, or business data, encryption is the silent guardian of our digital lives.
Let’s dive into how this technology works and why it’s essential for everyone in today’s interconnected world.

What is Data Encryption?
Data encryption is defined as the process of transforming readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) to protect it from unauthorized access. This transformation ensures that only those who possess the correct decryption key will be able to access the original data.

Role of Data Encryption in Cybersecurity
- Prevents sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Ensures that the data has not been changed during transmission.
- Authenticates the identity of the parties involved in the communication.
- Provides proof of actions, which does not allow denial of sending data.
- Supports compliance with regulatory requirements on data protection.
Types of Encryption
Asymmetric Encryption
- Key Pair Usage: It uses a pair of keys, one public and the other private, meant for encryption and decryption to enhance security.
- Slower Speed: Generally slower than symmetric encryption, hence not preferable for large data transfers, but suitable for small datasets.
- Common Algorithm: It includes RSA and Diffie-Hellman, which are widely used for secure communication and digital signatures 13.
- Enhanced Security: Extra features of better security such as authentication, and non-repudiation, which ensure integrity along with origin verification.

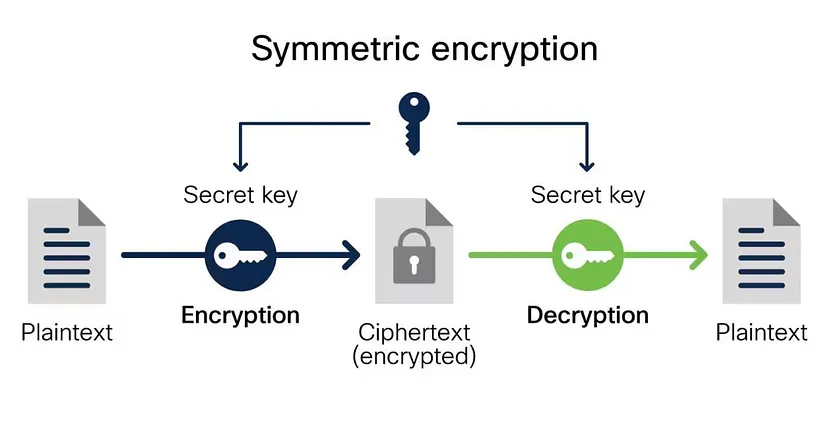
Symmetric Encryption
- Single Key Usage: Uses the same key for encryption and decryption, which means both parties must securely share that one key.
- Speed and Efficiency: It is generally faster and less resource-intensive than asymmetric encryption and thus suitable for encrypting large amounts of data.
- Common Algorithms: It includes algorithms such as AES, DES, and RC4, that are widely used for diverse applications.
- Key Management Challenges: The requirement to securely exchange and manage the secret key poses risks if the key is intercepted
Some Common Encryption Algorithms:
Before we move ahead to the algorithms, you need to know a few terms that will help you to understand the algorithms better.
- A public key is a cryptographic key that can be freely shared with anyone.
- A private key is a cryptographic key that must be kept secret and known only to its owner.
- Block cipher is a type of encryption algorithm that operates on fixed-size blocks of data, transforming plaintext into ciphertext using a secret key.
- A 64-bit block refers to a fixed-size chunk of data that is 64 bits (8 bytes) long.
DES (Data Encryption Standard)
DES is a symmetric block cipher algorithm that operates on 64-bit blocks using a 56-bit key. DES encrypts data by a series of permutations and substitutions across 16 rounds. Because of its weaknesses, it has largely been replaced by more secure algorithms like AES.
RES(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
RSA is an asymmetric encryption method based on two keys: the public key for encryption and the private key for decryption. This security depends on the use of large prime numbers and has proven difficult to factor. Thus, RSA is considered reliable for sensitive information transferred on the internet. It is applied in secure data transmission, digital signatures, and protocols for key exchange.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
AES is a symmetric encryption technique that encrypts data within fixed blocks of 128 bits, depending on their key size at 128, 192, or 256 bits. Using a series of transformations- substitution and permutation over a variety of rounds from 10 to 14, depending on the size of the key.
Importance of Data Encryption

Data encryption is important to safeguard sensitive information in the present digital landscape. It can be summed up with three key benefits:
1. Data Protection: Encryption protects data from access by unauthorized parties. Therefore, even if a device is compromised, the information encrypted remains safe and not readable without the proper key. This is a preventive measure against data breaches when storing and transmitting data.
2. Privacy: Encryption helps maintain the confidentiality of personal and sensitive information since it restricts access to encrypted data, preventing entities like hackers or governments from intercepting and reading communications.
3. Compliance: Most industries have strict laws on data protection. Encryption helps organizations adhere to regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA, which require protecting sensitive data to avoid lawsuits and build trust with customers.
In actual applications, encryption is deployed in online banking transactions and secure communications, such as HTTPS, and also the protection of sensitive business information, making it the keystone of modern cybersecurity tactics.
How to Encrypt Your Data?
Start encrypting your data with these tools and tips:
Tools
VeraCrypt: A free and open-source tool for creating encrypted volumes and full disk encryption, which offers good protection for your files.
BitLocker: This is a Windows feature that encrypts entire drives to offer security against unauthorized access.
To learn about these tools click on the links given and you will be redirected to their website where you will find a lot of info about them.
Tips for Beginners
- Determine which files or folders contain sensitive information that needs protection.
- Always create complex passwords for your encryption keys to enhance security.
- Keep your encryption tools updated to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Ensure you have secure backups of your encrypted data in case of hardware failure or loss.
I will conclude all this by saying start encrypting your data and stay protected. As the world is digitalizing cyber threats are increasing very rapidly so stay one step ahead of Cybercriminals in this Cyber World and start encrypting your data.




Pingback: Best Browser Extensions for Privacy - Cynfober